NPDB Guide to Reporting Civil Judgments
Infographics provide basic guidance only. Review federal regulations and the NPDB Guidebook for comprehensive instructions.
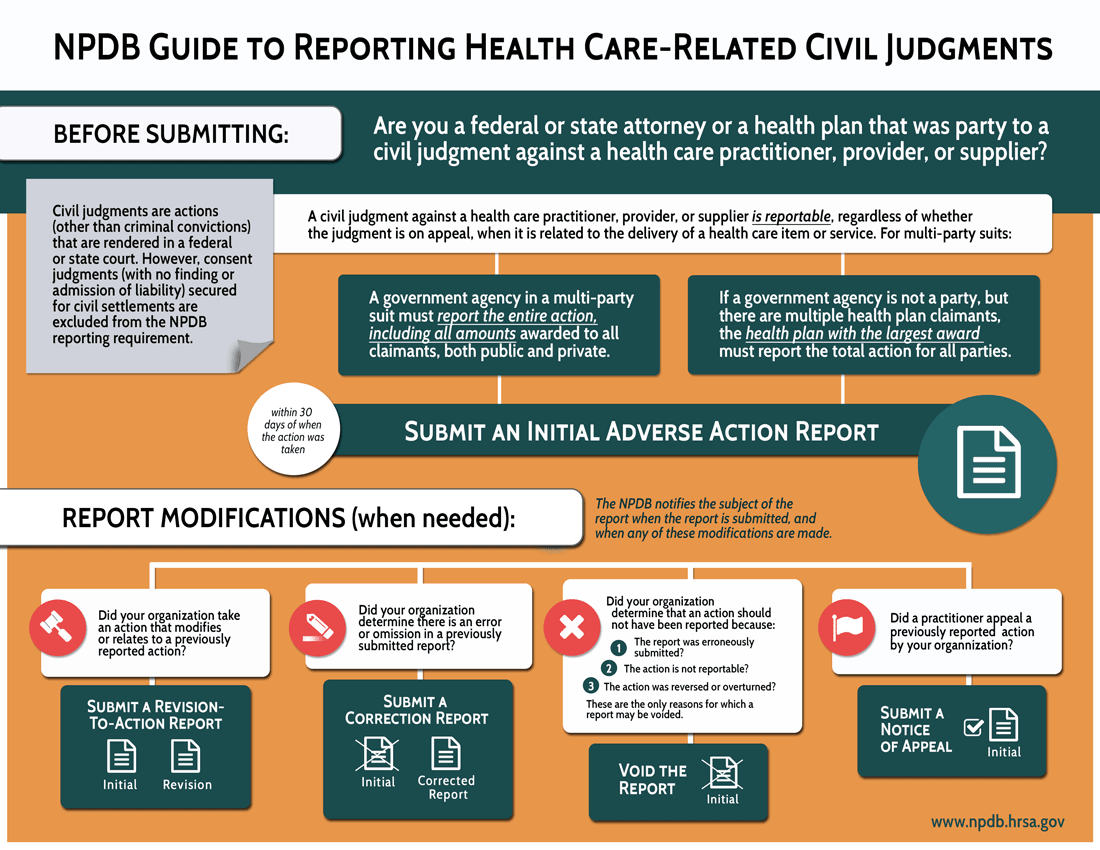
NPDB Guide to Reporting Civil Judgments
Before Submitting:
Are you a federal or state attorney or health plan that was party to a civil judgment against a health care practitioner, provider, or supplier?
Civil judgments are actions (other than criminal convictions) that are rendered in a federal or state court. However, consent judgements (with no finding or admission of liability) secured for civil settlements are excluded from the NBPDB reporting requirements.
A civil judgment against a health care practitioner, provider, or supplier is reportable, regardless of whether the judgment is on appeal, when it is related to the delivery of health item or service. For multi-party suits:
- A government agency in a multi-party suit must report the entire action, including all amounts awarded to all claimants, both public and private.
- If a government agency is not a party, but there are multiple health plan claimants, the health plan with the largest award must report the total action for all parties.
Submit an Initial Adverse Action Report within 30 days of when the action was taken
Report Modifications (when needed):
The NPDB notifies the subject of the report when the report is submitted, and when any of these modifications are made.
- Did you organization take an action that modifies or relates to a previously reported action (including reinstatements)? If yes, Submit a Revision to Action report.
- Did your organization determine there is an error or omission in a previously submitted report? If yes, submit a Correction Report.
- Was it determined that an action should not have been reported because:
- The report was erroneously submitted?
- The action is not reportable?
- The action was revered or overturned?
- Did a practitioner appeal a previously reported action? Submit a Notice of Appeal
View a PDF Version (PDF - 146 KB)
 An official website of the United States government.
An official website of the United States government.

